Prevent gum disease damage with early detection and good dental hygiene. Gum disease is particularly risky because it often develops without pain and goes unnoticed until it causes serious issues.
Periodontal Treatment & Preventive Care
The most effective way to handle periodontal issues is through prevention. Your personalized "check up" helps protect you from gum disease (periodontal disease and gingivitis), tooth decay, and stress-related problems such as teeth grinding and TMJ.
Periodontal exam
During your visit, we will check your mouth for signs of periodontal disease. Early diagnosis and treatment are very important for your dental and overall health.
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, is an infection that affects the bone and supporting structures of your teeth. It is estimated that 80% of the adult population has some level of gum disease.
Periodontal bacteria can initiate an inflammatory response that damages the tissue connecting teeth to the bone. This tissue loss creates a space called a periodontal pocket. While everyone has some level of pocketing, normal depths are between 1 and 3 mm. Daily brushing and flossing help keep these pockets clean. However, in cases of periodontal disease, the pockets can be deeper than 3 mm, making them harder to clean and maintain. As a result, bacteria and debris build up at the bottom of the pocket, leading to chronic gum infection.
As we age, we become more vulnerable to periodontal bacteria, and poor hygiene or cleaning is another cause of periodontal disease. Without treatment, teeth will lose enough support to become loose and painful, eventually leading to tooth loss.
Periodontal disease affects your entire body!
Chronic gum infection, especially inflammation, affects all organ systems. Recent peer-reviewed studies show individuals with chronic periodontal disease have a two- or threefold increased risk of stroke, heart disease, and diabetes. Other issues include gastric ulcers, osteoporosis, and preterm babies.
The best way to avoid problems like these is to take care of your gums.
Stages of periodontal disease
-
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease. Gums become tender, swollen, and prone to bleeding. This can usually be stopped with proper oral hygiene and treatment from your dentist.
-
Moderate Periodontitis
In the moderate stage of gum disease, the gums deteriorate and start detaching from the teeth, forming gum pockets that allow plaque to accumulate below the gum line. This exposes the tooth roots to a higher risk of decay.
-
Advanced Periodontitis
This is an advanced stage of gum tissue and bone loss. Teeth become loose and may even need to be pulled. This makes it hard to chew and bite normally. If advanced periodontal disease is left untreated, patients face the risk of other serious health problems.
Periodontal treatments for gum disease
-
Tooth Scaling
Scaling is necessary when plaque and tartar are present at or below the gum line. Then, plaque and tartar are scraped from the tooth’s crown and root.
-
Root Planing
In many cases, root planing smooths the surface of the tooth after scaling.
-
Medication
Antibiotics or irrigation with antimicrobial agents, such as chemical solutions or mouth rinses, may also be necessary to help control the growth of bacteria that produce toxins and cause periodontitis.
-
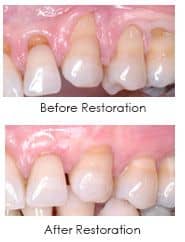
Tissue Graft
Gum tissues around the necks of teeth often recede due to periodontal disease, genetically inherited thin tissue, or aggressive brushing. This recession can cause tooth roots to become sensitive to cold. We offer various periodontal tissue augmentation procedures that can cover exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and improve appearance. Besides enhancing aesthetics, these tissue grafting procedures create a thicker band of tissue around the treated teeth, helping to improve their long-term outlook.